Web and Mobile Applications
Suppose you wanted to define and solve a model in a mobile application written in JavaScript. Powerful
optimizers that would run directly on a mobile device aren't available, nor would they be the best solution.
But it's simple to send a model to the RASON REST Server and get the optimal solution for an optimization
model, the expected mean for a simulation model, or a data science model (or forecasting model) fit to a training
partition.
var request = {
"variables" : { ...
"obj" : { formula:"z", "type": "minimize", "finalValue": [] }
}
};
$.post("https://rason.net/api/optimize", JSON.stringify(request)).done(function(response) {
alert(response.objective.z.finalValue);
});
Since RASON models are valid in JSON, we can write the entire model as an object constant in
JavaScript, assigned to the variable request. Then (using JQuery syntax) we make an AJAX
request to the RASON Server's REST API endpoint optimize, which means "optimize this model
and immediately return the result." When the server returns a response, the "done" function is called,
and it can easily reference the final value of the objective, since the response is also JSON.
Using the RASON Web IDE, we can perform the same actions as in the code segment above, by simply clicking
the button labeled POST rason.net/api/optimize.
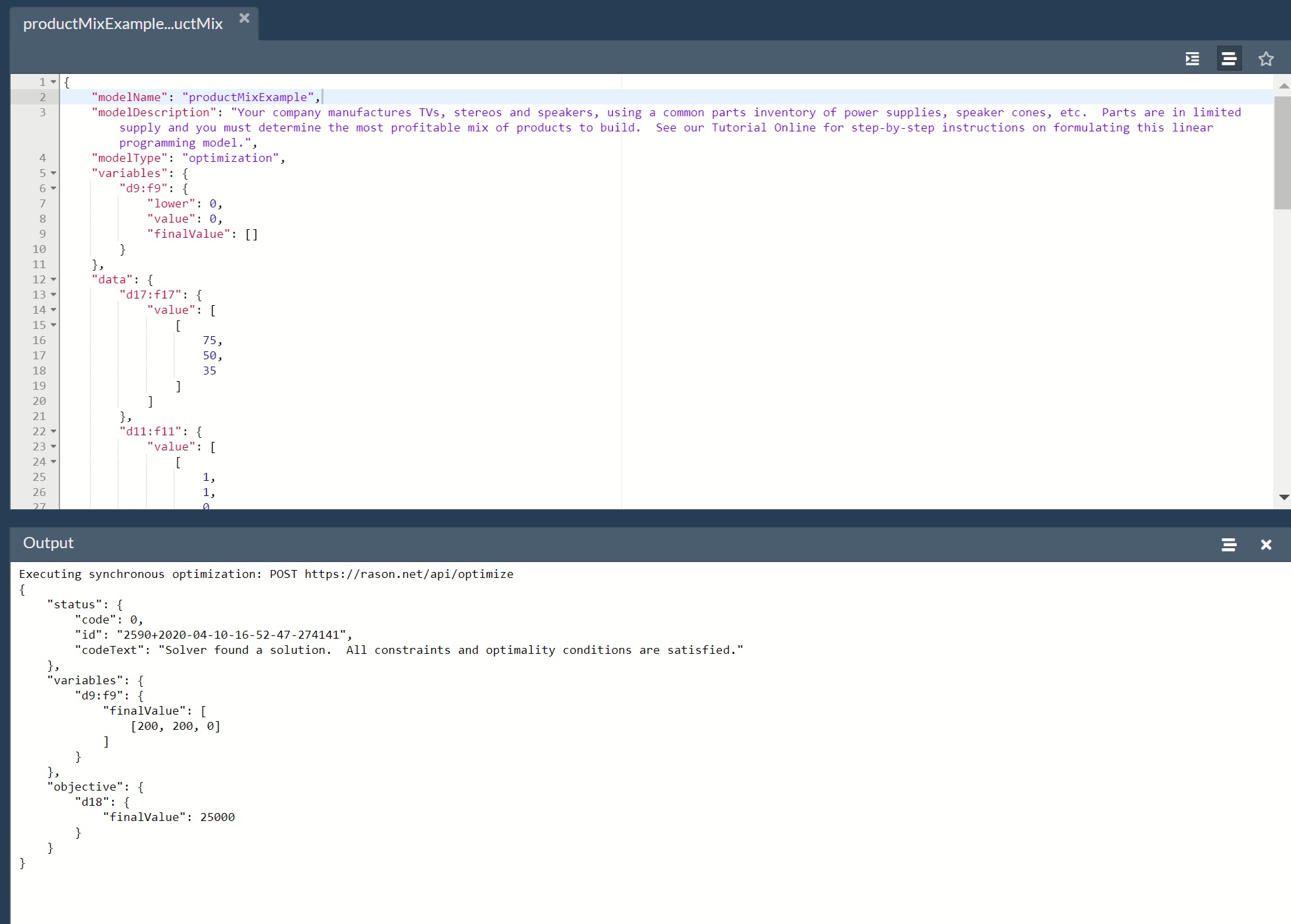
What about a mixed-integer or global optimization model, large simulation or Big Data model that might take 30
minutes - or overnight - to run? That's easy: With POST to rason.net/api/model, you can create a
"model resource," then start an optimization via GET/POST rason.net/api/model/id/optimize, check on
its progress at any time with GET rason.net/api/model/id/status and obtain results when finished
with GET rason.net/api/model/id/result.
Back to A Decision Table Example Model
|