Introduction to Defining Decision Tables in RASON
Users of RASON have the ability to create and evaluate Decision Tables. A decision table contains a set of rules which specify actions to perform
based on specific conditions. Decision tables are a good tool to use when there is a consistent number of rules, or conditions, to be evaluated
followed by a specific set of actions to be performed once a rule, or condition, is met. For example, the simple decision table below returns an
employee's pay based on the number of hours worked.
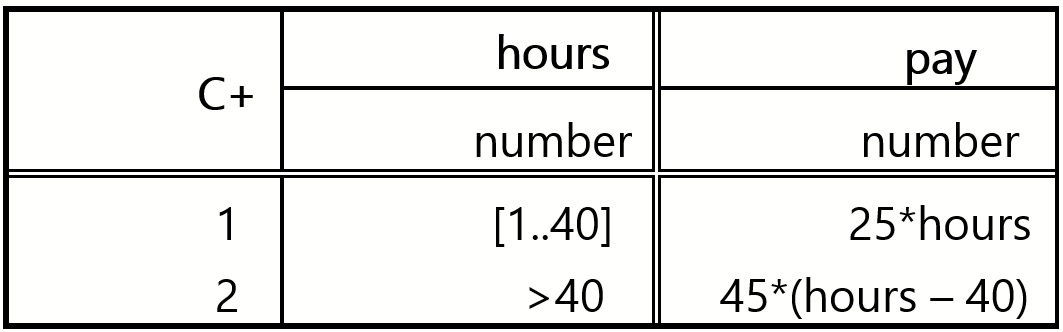
If the employee worked from 1 to 40 hours in a week, the pay is $25 * hours. If any overtime is worked, the employee gets paid $45 an hour for any
hour above 40.
A RASON decision table has a name, input/output parameters and a body implementing the logic through a structured framework. In RASON, a decision
table is created in the decisionTable section.
This same decision table written in the RASON modeling language is below.
{
modelName: "DTIntro",
modelType: "calculation",
decisionTables: {
"tblPayDay": {
inputs: ["hours"],
outputs: ["pay"],
refTypes: ["number", "number"],
hitPolicy: "C+",
rules: [
["[1..40]", "25 * hours"],
[">40", "45*(hours – 40)"]
]
}
},
Use the formulas section to calculate the decision table given the input parameter, hours = 45.
formulas: {
"paycheck": {formula: "tblPayDay(,,45)", comment: "calculate pay per employee", finalValue:[]}
}
}
The modeling language inside of Rason's Decision Table functionality is S-FEEL extended to standard conversion functions in FEEL. For more information on Decision Tables, we invite you to reference the following: DMN Method and Style by Bruce Silver (Cody Cassidy Press, September 28, 2018 and DMN Cookbook by Bruce Silver & Edson Tirelli (Cody-Cassidy Press, April 4, 2018).
|